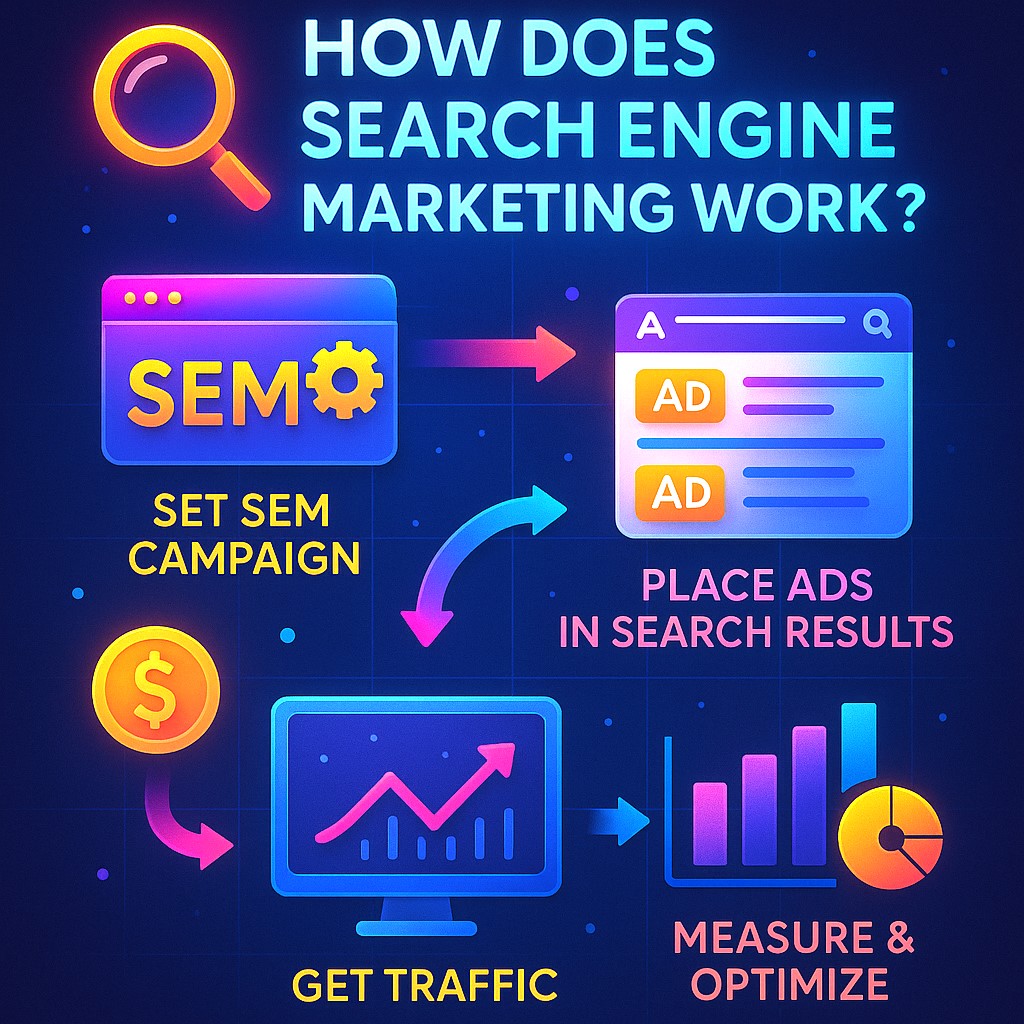
How Does Search Engine Marketing Work ?

Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is one of the most powerful tools in digital marketing. It allows businesses to promote their products or services directly in search engine results, targeting users actively looking for related information. This article explains how SEM works, including its core components, how ads are placed, and how businesses can use SEM to drive measurable results.
What Is Search Engine Marketing?
Search Engine Marketing is a form of online advertising where marketers pay to display their website in search engine results pages (SERPs). This strategy places ads prominently above or beside organic results when users enter specific keywords. Unlike Search Engine Optimization (SEO), which focuses on organic rankings over time, SEM delivers immediate visibility through paid placements.
The goal of SEM is to attract users who are already searching for something relevant to what the business offers. These users tend to have higher intent, making SEM a high-converting channel when executed properly.
Key Components of SEM
To understand how SEM works, it’s essential to break down its major components:
1. Keyword Research
Everything starts with keywords. Businesses identify terms and phrases that their potential customers are likely to type into a search engine. These keywords are the foundation of every SEM campaign. Marketers use keyword research tools to analyze search volume, competition, and user intent.
For example, if a company sells running shoes, they may target keywords like “best running shoes for flat feet” or “affordable running shoes online.” Choosing the right keywords ensures the ad is shown to the right audience.
2. Ad Auction
Every time someone enters a search query, an instant auction determines which ads appear. This auction isn’t just based on who pays the most. It considers:
-
Bid amount – How much the advertiser is willing to pay per click.
-
Quality score – A rating based on ad relevance, expected click-through rate, and landing page experience.
-
Ad extensions and format – Additional information such as links, phone numbers, or locations that enhance the ad.
Search engines combine these factors to determine Ad Rank, which influences where and if the ad will appear.
3. Ad Creation
Marketers create compelling text ads designed to encourage users to click. A standard search ad includes:
-
A headline (often split into two or three parts)
-
A display URL
-
A brief description
-
Optional extensions (e.g., location, callout, sitelinks)
The goal is to make the ad relevant, engaging, and action-oriented, such as using calls to action like “Buy Now” or “Get a Free Quote.”
4. Landing Page Optimization
When a user clicks on an ad, they are taken to a landing page. This page must match the ad’s intent and provide a clear, seamless user experience. A well-optimized landing page includes:
-
A relevant headline
-
Clear product or service information
-
Fast loading speed
-
Mobile-friendly layout
-
A strong call-to-action (CTA)
The landing page is crucial because it impacts both the conversion rate and the ad’s quality score.
The SEM Process: Step by Step
Let’s look at how SEM typically works from planning to execution.
Step 1: Define Goals
Before launching any SEM campaign, a business needs clear goals. These could include increasing website traffic, generating leads, driving product sales, or promoting a new service.
Step 2: Conduct Keyword Research
Using keyword tools, the business identifies high-intent keywords that match its offerings. These keywords are categorized into ad groups for better targeting.
Step 3: Create Campaigns and Ad Groups
Each campaign targets a specific objective and may include multiple ad groups. Each ad group focuses on a set of related keywords and serves tailored ads.
Step 4: Write Ads
Ad copy is crafted based on user intent. Ads must be relevant to the keywords and offer a compelling value proposition. This includes writing effective headlines, using strong CTAs, and including ad extensions.
Step 5: Set Budget and Bids
Advertisers decide how much they’re willing to spend daily or monthly and how much to bid per click. Bidding strategies can be manual or automated, depending on the campaign goals.
Step 6: Launch and Monitor
Once live, the campaign enters the ad auction every time a matching search occurs. Performance data is tracked in real-time.
Step 7: Optimize Continuously
Successful SEM requires ongoing optimization. This includes:
-
A/B testing different ad variations
-
Adjusting keyword bids
-
Pausing underperforming keywords
-
Improving landing pages
-
Refining targeting by device, location, and time
Benefits of SEM for Businesses
SEM offers several unique advantages over other marketing channels:
1. Immediate Results
Unlike SEO, which can take months to show progress, SEM allows your business to appear in search results almost instantly after launching a campaign.
2. Targeted Reach
SEM ensures your ads are shown to people already searching for related products or services. This means higher chances of conversions.
3. Cost-Effective
You only pay when someone clicks your ad (Pay-Per-Click model), ensuring your budget goes toward actual engagement rather than impressions alone.
4. Measurable ROI
Every aspect of an SEM campaign can be tracked—clicks, impressions, conversion rates, cost per lead, etc.—allowing data-driven decisions.
5. Brand Visibility
Even if users don’t click on the ad, your brand gains exposure by appearing at the top of the search results.
Common Challenges in SEM
While SEM is powerful, it also has challenges that marketers must address:
-
High competition – Popular keywords are expensive and competitive.
-
Ad fatigue – Users may get used to seeing the same ads and stop clicking.
-
Budget limits – Small businesses may struggle to compete with larger companies.
-
Constant changes – Algorithms and ad policies can shift frequently, requiring ongoing learning.
These challenges require consistent monitoring, strategic planning, and adapting to market trends.
Best Practices for Effective SEM Campaigns
To make the most out of your SEM efforts, follow these proven strategies:
-
Use long-tail keywords to target more specific, lower-competition searches.
-
Regularly update your negative keyword list to avoid irrelevant traffic.
-
Keep testing different ad copy variations to improve performance.
-
Ensure your landing pages match ad intent and are optimized for speed and mobile use.
-
Leverage ad scheduling to show your ads when your audience is most active.
-
Analyze and refine your conversion tracking to measure what truly drives results.
Conclusion: How SEM Works in Today’s Digital Market
Search Engine Marketing works by targeting users at the exact moment they’re searching for a product, service, or solution. Through a combination of keyword targeting, paid ad placement, and data-driven optimization, businesses can drive traffic and sales quickly and efficiently.
While SEM can be complex and competitive, its potential return makes it a vital part of any comprehensive marketing strategy. With the right approach—focused on relevance, user experience, and ongoing performance tracking—businesses can achieve substantial growth through search engine marketing.