Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing Examples
As technology continues to evolve, two powerful computing paradigms are transforming how businesses and individuals process data: edge computing and cloud computing. While both serve the purpose of managing and analyzing data, they do so in very different ways. Understanding the distinction between them is essential for anyone involved in IT, digital transformation, or emerging tech.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into edge computing vs cloud computing examples, explore how they function in real-world scenarios, and help you understand which one is best suited for specific applications.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the use of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data. Instead of maintaining physical infrastructure locally, users can access computing power on demand through a centralized cloud provider.
The main advantages of cloud computing include:
-
Scalability – Easily scale up or down based on demand.
-
Cost Efficiency – Pay only for the resources you use.
-
Accessibility – Data and applications are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
-
Centralized Management – Easier to manage security, updates, and performance.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing, on the other hand, processes data at or near the source where it is generated — such as sensors, smart devices, or local servers. This approach reduces latency and decreases the need to send large volumes of data back to a central cloud system.
Benefits of edge computing include:
-
Low Latency – Faster data processing and real-time decision-making.
-
Reduced Bandwidth Use – Only essential data is sent to the cloud.
-
Increased Privacy – Sensitive data can be processed locally.
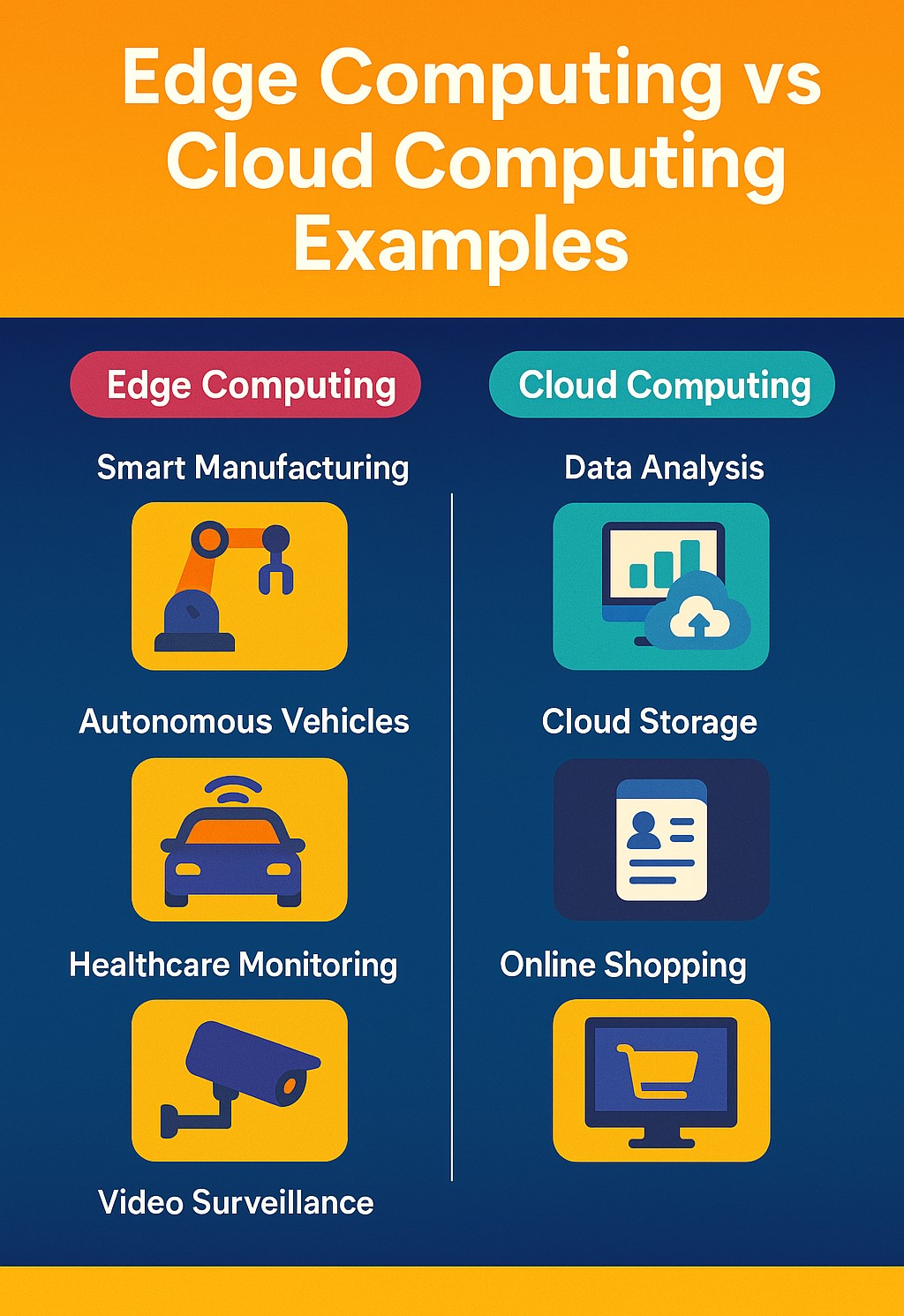
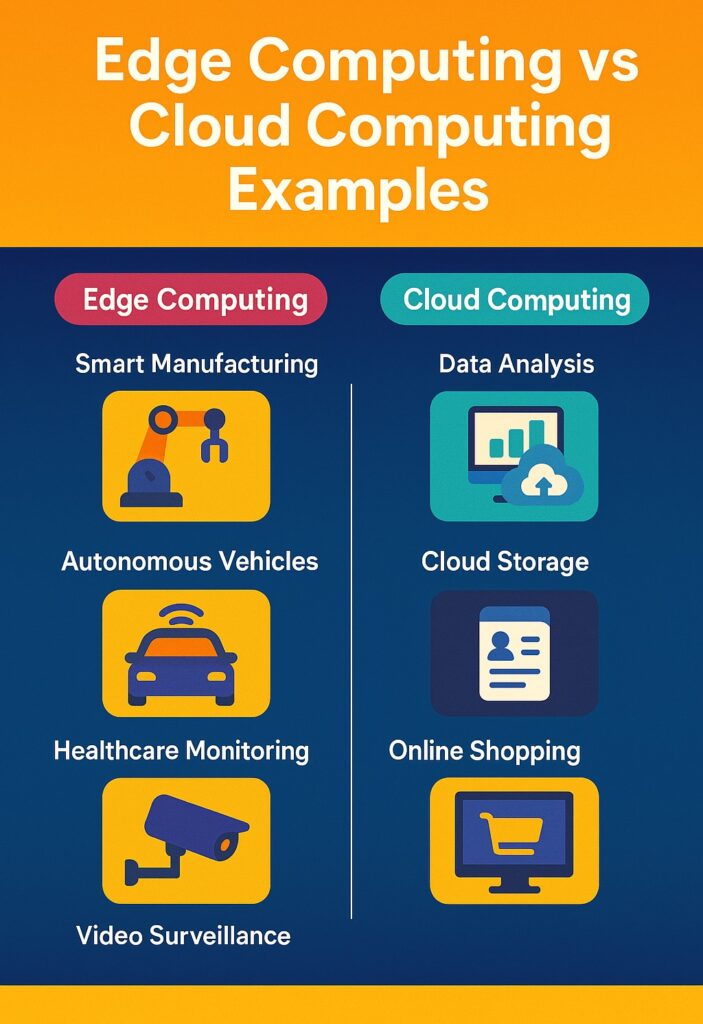
Real-World Example #1: Smart Manufacturing
Edge Computing Example:
In a smart factory, machines are equipped with sensors that monitor temperature, vibration, and speed. Edge computing devices analyze this data on-site in real time to predict equipment failures before they happen.
-
Benefit: Immediate response to anomalies without waiting for cloud processing.
-
Result: Reduced downtime and improved efficiency.
Cloud Computing Example:
The same factory uploads production data to the cloud every night for long-term analysis and reporting. Managers use cloud dashboards to view trends and make strategic decisions.
-
Benefit: Scalable data storage and high-level insights.
-
Result: Better planning and predictive maintenance over the long term.
Real-World Example #2: Autonomous Vehicles
Edge Computing Example:
Autonomous vehicles use edge computing to process sensor data (like cameras, radar, and LIDAR) in real time. The vehicle must make split-second decisions without relying on a remote server.
-
Benefit: Millisecond-level response time.
-
Result: Safer driving decisions and fewer accidents.
Cloud Computing Example:
The vehicle sends driving data to the cloud for training artificial intelligence models. Developers analyze this data to improve algorithms and software updates.
-
Benefit: Centralized learning and updates.
-
Result: Continuous improvement of driving behavior.
Real-World Example #3: Healthcare Monitoring
Edge Computing Example:
A wearable health device monitors a patient’s heart rate and detects irregularities locally. If a serious condition is detected, the device immediately alerts the patient or a caregiver.
-
Benefit: Instant response in emergency situations.
-
Result: Life-saving interventions without delay.
Cloud Computing Example:
The patient’s long-term health records are stored in the cloud. Doctors access the data remotely for checkups, trend analysis, and diagnosis.
-
Benefit: Easy access to historical data.
-
Result: Better long-term care and treatment planning.
Real-World Example #4: Video Surveillance
Edge Computing Example:
Security cameras use edge computing to detect motion or recognize faces in real time. Only relevant video clips are saved or transmitted, rather than hours of footage.
-
Benefit: Real-time threat detection and lower storage needs.
-
Result: Faster incident response and more efficient data handling.
Cloud Computing Example:
Surveillance footage is archived in the cloud for compliance and review. Users can search and access footage remotely from different locations.
-
Benefit: Centralized access and scalability.
-
Result: Improved oversight and easy retrieval of past footage.
Real-World Example #5: Retail and Customer Experience
Edge Computing Example:
In a smart retail store, edge devices analyze foot traffic patterns and shelf activity in real time. The system automatically adjusts digital signage or restocks shelves based on customer movement.
-
Benefit: Immediate personalization and operational efficiency.
-
Result: Enhanced customer experience and higher sales.
Cloud Computing Example:
Sales data, inventory levels, and customer profiles are synced to the cloud. This data is used for forecasting, loyalty programs, and multi-store coordination.
-
Benefit: Centralized intelligence across all store locations.
-
Result: Informed marketing and supply chain decisions.
Key Differences Summarized
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing Location | Near data source (locally) | Remote data centers |
| Latency | Low | Higher (due to network delays) |
| Real-Time Capability | Excellent | Limited |
| Bandwidth Needs | Low | High |
| Scalability | Limited to local resources | Virtually unlimited |
| Security | Data stays on-site | Centralized, but potentially more exposed |
| Use Cases | Autonomous systems, IoT, emergency services | Big data, web apps, analytics |
Which One Should You Use?
Both edge and cloud computing offer unique advantages. The right choice depends on your application needs:
-
Choose Edge Computing if you require real-time response, low latency, and offline capability.
-
Choose Cloud Computing if you need scalability, centralized management, and deep analytics.
In many cases, businesses use a hybrid approach — combining edge for immediate processing and cloud for long-term storage and analysis.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the practical applications of edge computing vs cloud computing examples helps clarify how these technologies work in the real world. From healthcare to retail to autonomous vehicles, both systems offer critical advantages that solve different problems.
As digital transformation continues, the integration of edge and cloud computing will become even more seamless. Knowing how and when to apply each approach will give your business a competitive edge in the age of smart technology.
✅ Key Takeaways
-
Edge computing processes data locally, close to the source, making it ideal for real-time applications with low latency needs.
-
Cloud computing handles data remotely on centralized servers, offering scalability, cost-efficiency, and access to powerful analytics tools.
-
Smart manufacturing, autonomous vehicles, healthcare devices, video surveillance, and retail systems all demonstrate how edge and cloud computing can be used together effectively.
-
Edge computing is best for time-sensitive decisions, such as detecting machinery faults or processing data in autonomous vehicles.
-
Cloud computing is ideal for storing large amounts of data, performing long-term analysis, and managing resources across multiple locations.
-
A hybrid approach, using both edge and cloud together, is becoming common to maximize performance, cost savings, and flexibility.
-
Choosing the right model depends on your specific business needs, especially around speed, bandwidth, data privacy, and computing power.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edge_computing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
Links License – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Text_of_the_Creative_Commons_Attribution-ShareAlike_4.0_International_License
Dear Friends, welcome you to check out tech products from my blog. Thanks For Your Support.
https://techsavvo.com/category/tech-products/